What is Diabetes and How can we Fight it?

Diabetes is a chronic disease that develops when our body, through the pancreas, does not produce enough insulin or can’t respond to it appropriately, leading to high levels of sugar in the blood. Originally a disease that only concerned rich countries it is now occurring more frequently in the middle and low-income countries, affecting adults and children indifferently, sparing no country nor social class. Thus, everyone can be affected by this epidemic which now is the concern of 415 million people worldwide, or 1 in 11 adults, making diabetes one of the 5 more common reasons for death.
Diabetes is a major threat to global health and it is important to bring awareness in order to better understand it and tackle it. That’s why in 1991, World Diabetes Day was created, happening since then every 14th of November.
Insulin and types of diabetes
Insulin is a hormone that regulates the metabolism of carbohydrates, fats and protein, by promoting the absorption of carbohydrates, especially glucose, from the blood into liver, fat and skeletal muscle cells. It plays such an important role in regulating sugar in our body that on people that suffer from diabetes and the pancreas is not able to produce any insulin or make proper use of it, it will lead to a rise in glucose levels in blood, called hyperglycemia, which can lead to many health problems that are explained later in the article.
Three main kinds of diabetes exist:
- Type 1 diabetes:
Previously known as insulin-dependent, juvenile or childhood-onset because it affects children and adolescents more frequently, it can be developed at any age. It is an autoimmune disease, as the body makes none or a very small amount of insulin, due to the immune system attacking and destroying the cells in the pancreas that produce it. So far, the causes for its appearance are still unclear and it can’t be prevented, but certain tendencies to genetic and environmental factors have been observed.
- Type 2 diabetes:
The most common one with 90% of all cases, formerly called non-insulin-dependent or adult-onset, is observed when the body doesn’t properly use insulin. Contrary to type 1diabetes it is not an autoimmune disease, meaning that the reason for its appearance, even in unknown cases, tends to be more related to genetics and a combination of an unhealthy lifestyle (like not exercising and being overweight).
- Gestational diabetes:
Developed by pregnant women, it's hyperglycemia is where blood glucose values are above normal but below those of diabetes diagnostics. Generally, it goes away with the delivery of the baby, although it sometimes leads to type 2 diabetes afterward. Its cause is the appearance of insulin-blocking hormones produced during pregnancy along with lifestyle factors.
Apart from these more common types of diabetes, other rare types exist due to other causes like drug or chemical-induced diabetes.
Symptoms and consequences
You can see the different symptoms of diabetes in the graph below:
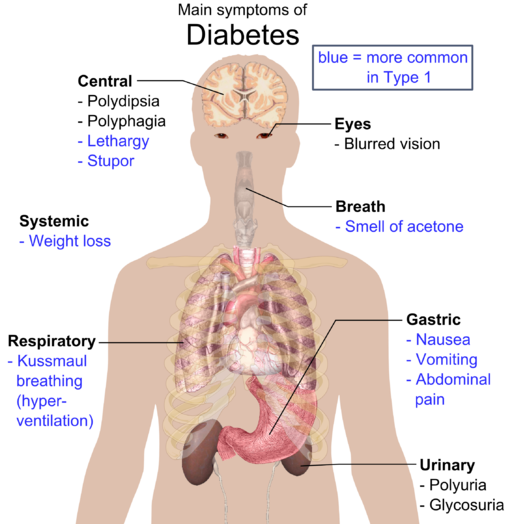
People suffering from diabetes have an increased risk as well to develop other complications due to their level of glucose in the blood. The more frequent are:
- Cardiovascular disease including strokes, which is the most common cause of death among people suffering from diabetes.
- Eye problems called diabetic nephropathy, but also cataracts that can occur earlier than generally. Glaucoma can be developed.
- Kidney disease that is painless until it reaches an advanced state, so this needs to be regularly checked.
- Dental issues that increased risks of tooth decay.
- Oral complications
- Nerve damage can occur in the sensory and motor nerves in every part of the body, including organs.
- Foot problems, which in fact reduce blood supply and nerve function and can delay healing, increasing the risk of infection and reducing feeling in the feet, which can lead to ulcers and structural foot problems.
Treatments
After the diagnosis of diabetes, which generally occurs with a blood sugar test, and the confirmation of what type is the patient suffering treatment will be started by the doctor. For type 1, the most common treatment is the prescription of an insulin injection as well as some physical activity. For people suffering from type 2, weight reduction is necessary with a combination of a specific diet with an exercise program, with diabetes medication sometimes prescribed, prescribing insulin if and when the medications turn out ineffective. Patients suffering from gestational diabetes will be treated by insulin during their pregnancy.
If all medical recommendations are followed, it should result not only in the reduction of glucose in the blood but as well, especially in type 2 diabetes patients, drastic changes in their lifestyle.
Prevention and recommendations
The International Diabetes Foundation gives 9 recommendations for a healthy diet, lowering the chances of diabetes:
- Choosing water, coffee or tea instead of fruit juice, soda, or other sugar-sweetened beverages.
- Eating at least three servings of vegetables every day, including green leafy vegetables.
- Eating up to three servings of fresh fruit every day.
- Choosing nuts, a piece of fresh fruit, or unsweetened yogurt for a snack.
- Limiting alcohol intake to a maximum of two standard drinks per day.
- Choosing lean cuts of white meat, poultry or seafood instead of red or processed meat.
- Choosing peanut butter instead of chocolate spread or jam.
- Choosing whole-grain bread, rice, or pasta instead of white or plain.
- Choosing unsaturated fats (olive oil, canola oil, corn oil, or sunflower oil) instead of saturated fats (butter, ghee, animal fat, coconut oil or palm oil).

For people suffering from diabetes type 2, it’s appearance could be prevented or delayed by:
- Losing weight, which is a main factor in diabetes prevention. Even 5 or 10% less of a person's weight would have a tremendous benefit on their health if the person succeeds in keeping it off.
- Eating a healthy diet, the key to lose weight, cutting sugar consumption as there is a lot of added sugar in already processed food. You can also use sugar substitutes, like our Lakanto products that contain no sugar, and most importantly, no glycemic effect.
- Being fit, practicing a regular physical activity that will help lose weight and lower blood sugar levels at the same time. You can start slowly at your rhythm and try to end having 30 minutes of exercise 5 times a week.
- Quitting smoking, as it can increase insulin resistance.
- Having regular health check-ups, as a lot of people ignore they suffer from diabetes, delaying any possible treatment.
Now that you are well-informed, you are ready to participate at the World Diabetes Day, changing your life for the better as well as bringing awareness about this disease, helping people to take care of their health.